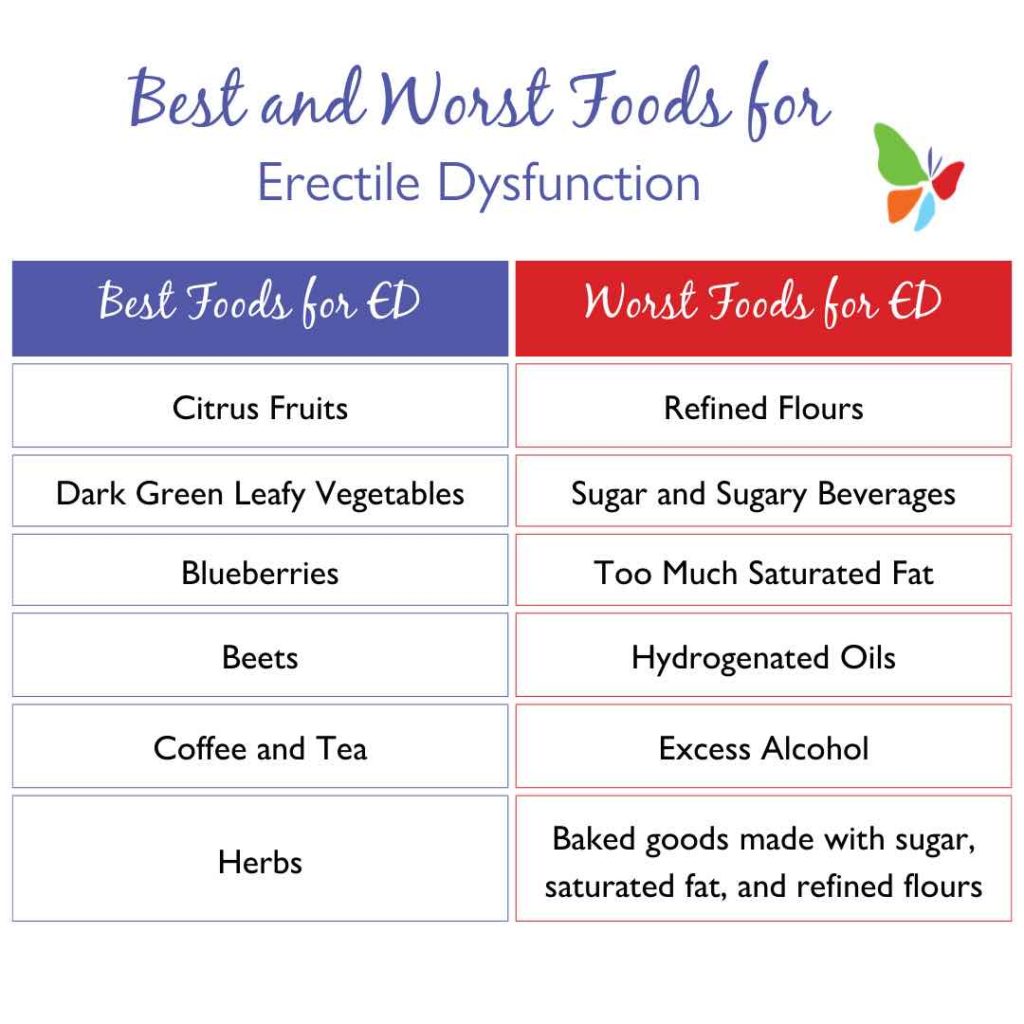
Don’t let your struggle with erectile dysfunction keep you down. This list of best and worst foods for ED will help prevent or alleviate these unwanted moments and keep you feeling your best!
The time-tested wisdom of, “Let Food Be Thy Medicine,” often gets overlooked for quick fixes. Food does more than curb appetite and prevent nutritional deficiencies such as scurvy, rickets, anemia, and xerophthalmia.
Western medicine now recognizes food as a functional ingredient to prevent and treat many diseases while promoting overall health. Current research overwhelmingly points to addressing lifestyle changes as the first plan of attack for comorbidities associated with ED. (1,2,5,6,7)
After a couple of clients hesitantly ask me if there are foods to cure erectile dysfunction, I knew this was a topic that needs to be spoken about more often and openly. And yes, there are both supplements and foods that can help prevent and treat ED, similar to how certain foods can help prevent heart disease and lower cholesterol. So, to start off, let’s cover a few “must-knows” about ED, then dive into what you can do to see a change.
How Many People Experience ED?
In the moment, it may feel as though erectile dysfunction is a solo problem. But, it’s more common than you think. After all, it’s not simply about getting your head in the game. Rather, this issue is both a physical and psychological condition that affects as many as 30 million men in the US. (1)
But let’s get something straight. Erectile dysfunction isn’t a problem limited to the “older” generation. As the saying goes, age is just a number. In fact, the overall prevalence of ED is estimated at 49.4% among men aged 40-88 years old. (2)
If you account for men experiencing ED as young as >20 years old, the incidence is 18.4%. So, with a little under one in five men battling erectile dysfunction, it’s time to address ways to prevent this unwanted issue.
Who Is at Risk For ED?
ED happens due to the decreased ability to dilate and augment flow in the small arteries. In other words, increasing blood flow will allow your body to rise to the occasion. And as you would guess, there are certain factors and health conditions that can impact this.
There’s a higher incidence of ED in:
- Older age groups
- People with medical conditions such as hypertension, type 2 diabetes, overweight, or obesity
- Smokers, vapers, or marijuana users
- Alcoholics or substance abusers
- People using certain medications
- People with psychological or emotional conditions
Although ED incidence increases with aging, the little blue pill doesn’t have to be a rite of passage as part of the normal aging process. Although, when indicated, it can be a game-changer.
The Best Food for Erectile Dysfunction
The good news is there are foods that help with erectile dysfunction. You can fuel your way to a better sex life, regardless of age. Start with embracing a Mediterranean-type diet. This fueling pattern is rich in plant-based ingredients that help improve blood flow, arterial flexibility, and chronic inflammation.
Low flavonoid, specifically flavone intake, is associated with ED in young adult men. (1) On the flip side, those who consume diets rich in flavonoids, anthocyanidins, and nitrate have decreased risk of ED. So, if it feels like an uphill battle, check out these must-try foods that help with erectile dysfunction.
Best Foods for ED
You may be wondering what foods help with erectile dysfunction. Here is a top list:
- Citrus fruits—oranges, lemons, and limes
- Dark green leafy vegetables—arugula, kale, and spinach
- Blueberries
- Beets
- Celery
- Red cabbage
- Broccoli
- Radish
- Coffee
- Tea—green, black, and oolong tea
- Herbs—parsley, peppermint, oregano, chamomile, mint, ginkgo biloba
- Fatty fish, like salmon
- Cocoa and cacao powder, or dark chocolate, at least 72%
- Grapes
- Cherries and chokecherries
- Black rice
- Purple rice
- Apples
- Tomatoes
- Onions
- Lettuce
- Red peppers
(4,8,9,10,11,12)
Worse Foods for Erectile Dysfunction
Don’t let your eating habits bring you down. Consuming excess amounts of these foods can increase the risk of inflammation, excess weight, cardiovascular disease, or type 2 diabetes—all of which may contribute to ED.
- Refined carbohydrates — white rice, processed flours
- Sugar and sugary beverages
- Baked goods made from refined sugars/flours—cookies, cakes, etc.
- Excess saturated fat—too much red meat, butter, and whole-fat dairy
- Hydrogenated oils
- Excess alcohol—especially above the daily limited recommendations (may experts now recommend no more than 1 drink a day for men). Give mocktails a try!
(13)
Phytonutrients and ED
What is common among the best foods for ED? They contain powerful phytonutrients and can provide or help boost nitric oxide. Let’s take a closer look at both.
It’s time to get intimate with phytonutrients! A healthful plant-based diet is associated with a decreased risk of erectile dysfunction. (10) But you don’t have to become a vegan or vegetarian to prevent ED. It’s all about boosting specific phytonutrients—mighty compounds that give plant-based foods their color, flavor, and health benefit.
First, eat more flavonoids – a type of polyphenolic compound. According to a study from the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, regular intake of these powerful nutrients is associated with reduced ED incidence in men less than 70 years old. Here are some examples of these phytonutrients:
| Phytonutrient Polyphenols | Food |
| Anthocyanins, Isoflavones, Quercetin | Apples, berries, citrus fruits, cocoa, coffee, grapes, green tea, peanuts, soybeans, and soy (edamame, tofu, soy milk), tea, whole grains, yams |
| Anthocyanins | Black rice, blueberries, cherries, chokecherries, grapes, oranges, radishes, and red cabbage. |
| Flavonoids (flavanones) | Citrus fruit, lemons, limes, oranges, grapefruit |
| Flavanols (Catechins) | Apples, berries, grapes, tea, green tea |
| Flavanols (Epigallocatechin Gallate) (ECGC) | Green tea |
| Isoflavonoids (Curcumin) | Cumin, turmeric |
| Flavanols (Quercetin) | Apples (near the skin), berries, cruciferous vegetables, broccoli, capers, gingko-biloba, grapes, honey, onions (outermost rings), and closest to root of red onion) shallot, tea, tomatoes |
| Isoflavones | Soybeans and soy products (edamame, tofu, soy milk) |
(8,9,14)

Foods that Boost Nitric Oxide for Erectile Dysfunction
Along with their other health benefits, greens can help you grow—all thanks to nitric oxide! Dark leafy greens contain dietary nitrate, which gets converted to nitrite within the body, followed by nitric oxide. This transformation process initiates with bacteria found under the tongue and within the stomach.
Tip: Skip the pre-game mouthwash to avoid killing these key players for nitric oxide production. It may also be a good time to skip garlic or onion-filled power fuel! (15)
But the benefits of nitric oxide don’t stop there! Research shows that nitric oxide derived from dietary nitrate plays an important role in cardiovascular health. Specifically, this nutrient may help reduce blood pressure, inhibit platelet aggregation, and increase blood flow. (15) Foods containing high-nitrate levels include:
- arugula
- spinach
- lettuce
- celery
- beetroot
- radish
Best Juice for Erectile Dysfunction
So that leaves the best juice for erectile dysfunction likely being beet juice—added benefit it’s beneficial for training and competitive fitness events. However, it’s a highly acquired taste. You can also buy it as a beet powder.

Tasty Recipes and Food Ideas to Boost Nitric Oxide Production
Although it’s not rocket science—nitric oxide may help your body lift off! So, eat more fruit and veggies and plant-based foods that help with erectile dysfunction. Not sure how to incorporate them into your daily habits? Check out these must-try tips. (14,16,17)
These foods can also help prevent the risk of certain comorbidities often seen with ED, such as high blood pressure, stiff arteries, blood clots, and type 2 diabetes. (18)
- Get Juicy! Include lime and lemon daily by adding lemon juice to foods like arugula salad, soups, tacos, fish, or plain water! Bonus. 4 oz a day of lemon juice can also help prevent kidney stones and so does eating a diet rich in fruits and veggies!
- Embrace the dark side of veggies. We’re talking leafy vegetables like arugula, kale, and spinach! These are also essential for your brain health!
- Eat more beets, celery, cabbage, broccoli, and radish. (14)
- Go coco for cacao (the less processed form of cocoa). When choosing a bar, aim for 72% or higher. Add cacao powder to oats, yogurt, smoothies, and more!
- Include salmon for its omega-3 fatty acids.
- Arugula or baby spinach salad – tossed with shaved parmesan, Myers lemon juice, salt and pepper.
- Roasted beets with vinaigrette or with fresh mozzarella or goat cheese
- Kale Apple Smoothie
- Blood Orange Fennel Salad (you can sub in other citrus)
- Cocoa Chia Pudding
- Blueberry Overnight Oats
Food vs. Medicine for ED
Unless there is a serious underlying health condition, there are plenty of preventative lifestyle approaches to give your buddy a helping hand without the need for medication. To put simply, these “magic pills” address the symptom, but behavioral changes attack the root cause.
As a registered dietitian well-versed in functional foods and supplements, proper nutrition and lifestyle management may give your body the lift it needs. But, if you are concerned about the possibility of a more serious condition, talk to your primary care providers or urologists to determine the appropriateness and necessity of medication.
Takeaways From Best and Worst Foods for ED
Addressing early prevention and underlying causes can help support an active sex life, which to no surprise, is associated with better mental health outcomes. After all, it’s a release in more ways than one!
Getting busy on the regular, ideally in a healthy loving relationship, can also help improve heart rate variability (HRV) and lower mortality risk. (5) However, it’s best to always address ED first with your primary care physician since it could indicate a more serious health condition, such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and hypertension. (1,2)
Use this article as your go-to resource for the best and worst foods for ED. Now it’s time to turn up the heat in the kitchen! Check back in and subscribe to our newsletter for upcoming content on supplements and lifestyle changes for ED.
Check out my books on plant-based eating! If you live in California book a nutrition counseling appointment today and take control of your health so you can live your best life!
References
- Nunes, Kenia Pedrosa, et al. “New Insights into Hypertension-Associated Erectile Dysfunction.” Current Opinion in Nephrology and Hypertension, vol. 21, no. 2, 2012, pp. 163–170., https://doi.org/10.1097/mnh.0b013e32835021bd.
- Grover, Steven A., et al. “The Prevalence of Erectile Dysfunction in the Primary Care Setting.” Archives of Internal Medicine, vol. 166, no. 2, 2006, p. 213., https://doi.org/10.1001/archinte.166.2.213.
- Mykoniatis, Ioannis, et al. “Sexual Dysfunction among Young Men: Overview of Dietary Components Associated with Erectile Dysfunction.” The Journal of Sexual Medicine, vol. 15, no. 2, 2018, pp. 176–182., https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsxm.2017.12.008.
- Hostetler, Gregory L, et al. “Flavones: Food Sources, Bioavailability, Metabolism, and Bioactivity.” Advances in Nutrition: An International Review Journal, vol. 8, no. 3, 2017, pp. 423–435., https://doi.org/10.3945/an.116.012948.
- Liu, Hui, et al. “Is Sex Good for Your Health? A National Study on Partnered Sexuality and Cardiovascular Risk among Older Men and Women.” Journal of Health and Social Behavior, vol. 57, no. 3, 2016, pp. 276–296., https://doi.org/10.1177/0022146516661597.
- Selvin, Elizabeth, et al. “Prevalence and Risk Factors for Erectile Dysfunction in the US.” The American Journal of Medicine, vol. 120, no. 2, 2007, pp. 151–157., https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2006.06.010.
- https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/urologic-diseases/erectile-dysfunction/definition-facts#:~:text=ED%20is%20very%20common.,men%20in%20the%20United%20States.&text=Although%20erectile%20dysfunction%20(ED)%20is,health%20care%20professional%20about%20treatment, Accessed 5/14/2022
- Tiwari, Brijesh K., et al. Handbook of Plant Food Phytochemicals: Sources, Stability and Extraction. Wiley-Blackwell, 2013.
- Panche, A. N., et al. “Flavonoids: An Overview.” Journal of Nutritional Science, vol. 5, 2016, https://doi.org/10.1017/jns.2016.41.
- Carto, Chase, et al. “Consumption of a Healthy Plant-Based Diet Is Associated with a Decreased Risk of Erectile Dysfunction: A Cross-Sectional Study of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.” Urology, vol. 161, 2022, pp. 76–82., https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2021.12.021.
- Cassidy, Aedín, et al. “Dietary Flavonoid Intake and Incidence of Erectile DYSFUNCTION1.” The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, vol. 103, no. 2, 2016, pp. 534–541., https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.115.122010.
- Olabiyi, Ayodeji A., and Kayode Ajayi. “Diet, Herbs and Erectile Function: A Good Friendship!” Andrologia, vol. 54, no. 6, 2022, https://doi.org/10.1111/and.14424.
- DeLay, Kenneth J, et al. “Modifying Risk Factors in the Management of Erectile Dysfunction: A Review.” The World Journal of Men’s Health, vol. 34, no. 2, 2016, p. 89., https://doi.org/10.5534/wjmh.2016.34.2.89.
- Halas M. (2019) Part 5: Phytonutrients.The Plant-Based Boost Nutrition Solutions for Athletes and Exercise Enthusiasts. 2019
- Ma, Linsha, et al. “Nitrate and Nitrite in Health and Disease.” Aging and Disease, vol. 9, no. 5, 2018, p. 938., https://doi.org/10.14336/ad.2017.1207.
- Davies, Kelvin P. “Development and Therapeutic Applications of Nitric Oxide Releasing Materials to Treat Erectile Dysfunction.” Future Science OA, vol. 1, no. 1, 2015, https://doi.org/10.4155/fso.15.53.
- Ma, Linsha, et al. “Nitrate and Nitrite in Health and Disease.” Aging and Disease, vol. 9, no. 5, 2018, p. 938., https://doi.org/10.14336/ad.2017.1207.
- Sullivan, M. “Nitric Oxide and Penile Erection: Is Erectile Dysfunction Another Manifestation of Vascular Disease?” Cardiovascular Research, vol. 43, no. 3, 1999, pp. 658–665., https://doi.org/10.1016/s0008-6363(99)00135-2.